Categories
Traceroute:
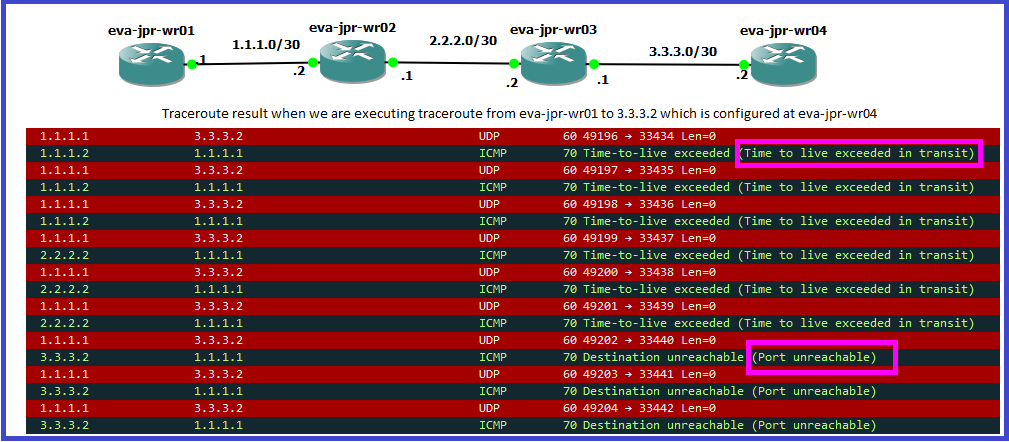
Traceroute is a tool or diagnostic utility which is used to identify the path used by a packet to reach destination. In Cisco network, traceroute uses a mix of UDP and ICMP packets.
How Traceroute works?
1. When we execute a traceroute command, Source sends three UDP packets with TTL of 1 towards Destination as below: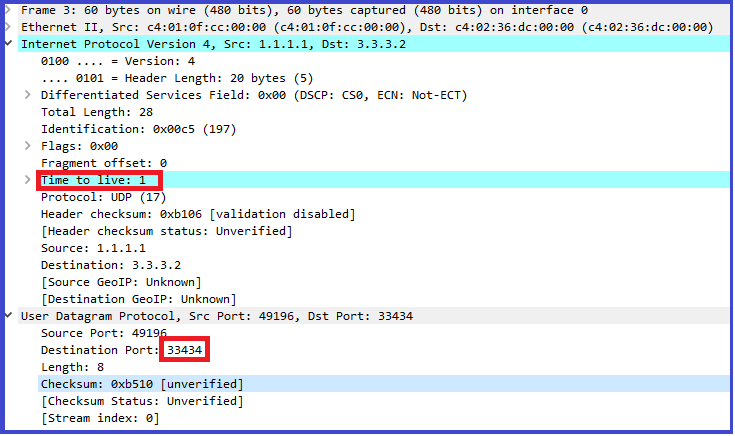
2. First router or Layer 3 hop, decrements the TTL of the packet by 1 therefore TTL hits 0,thus dropping it as a default behavior. router returns ICMP TTL Exceeded.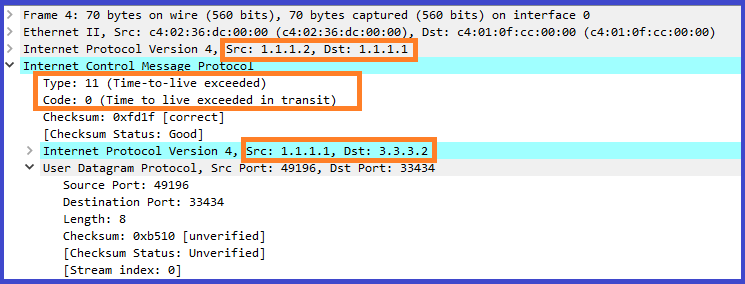
3. Once source device received the 3 ICMP TTL exceeded packets, it will send another 3 UDP packets with a TTL of 2. The same process recurs until the destination is reached.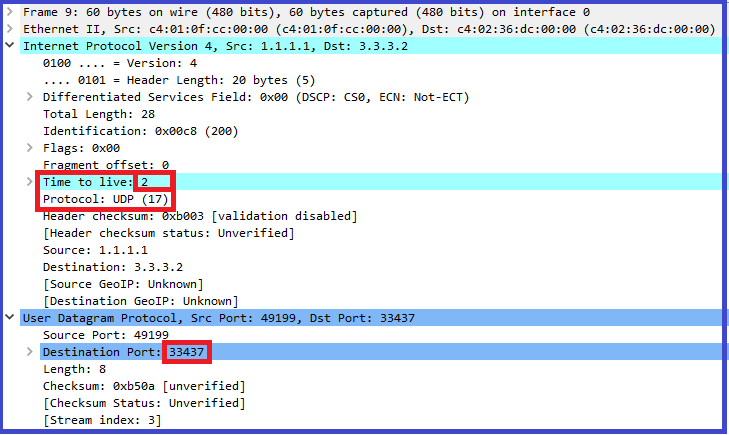
4. When Destination device receives packet then it returns ICMP Destination Unreachable (ICMP type 3, code 3) instead of the time to live exceeded messages as it requested for unknown port.
5. The traceroute process then knows that it reached the destination and the process can be stopped.
Ping:
Ping is utility which is used to check connectivity between devices over the network.
How ping works?
Ping uses the ICMP protocol. the source will send an ICMP ECHO request to destination device and wait for the destination to respond back with a ECHO reply..
1. Source generate a ICMP message which is encapsulated in IP datagram. Please find the below capture.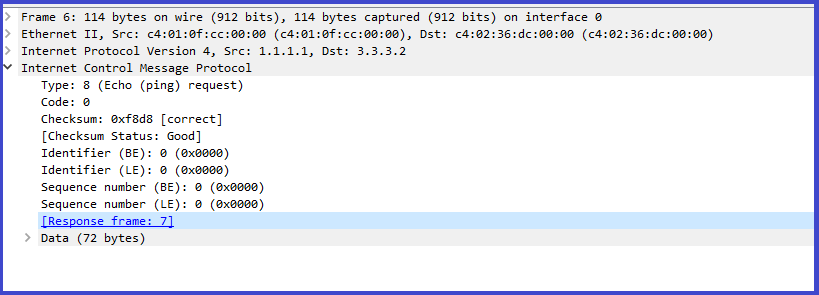
2. When destination receives it, sees the destination address and sends a ECHO reply back to originating Device. Please find the capture for your reference.
What happens when we access a device by name or browsing something?
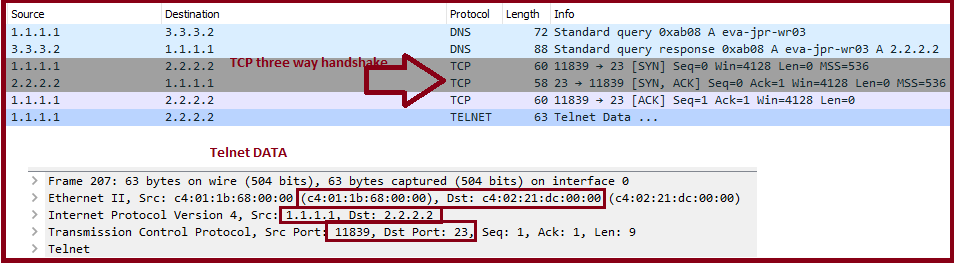
Let’s assume we are trying to telnet eva-jpr-wr03 from eva-jpr-wr01, below things are going to happens:
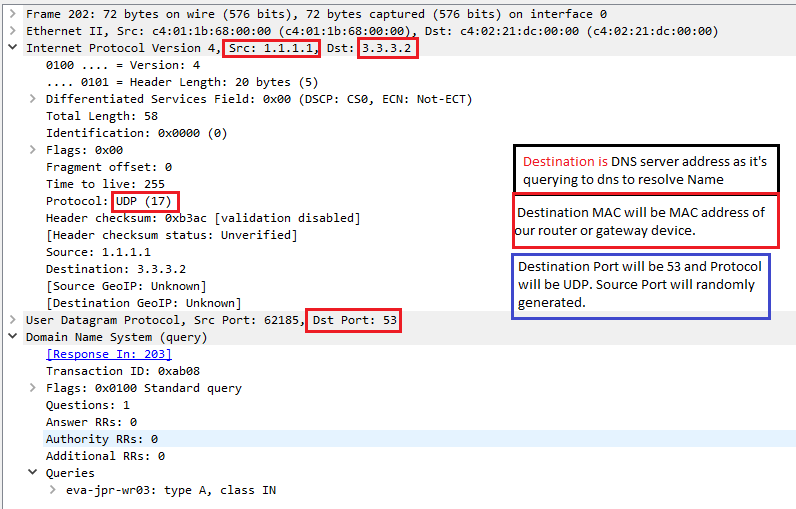
1) eva-jpr-wr01 will resolve eva-jpr-wr03 to an IP address using DNS. Device uses dns cache(browser/OS/Router cache) or sends a query to DNS server.
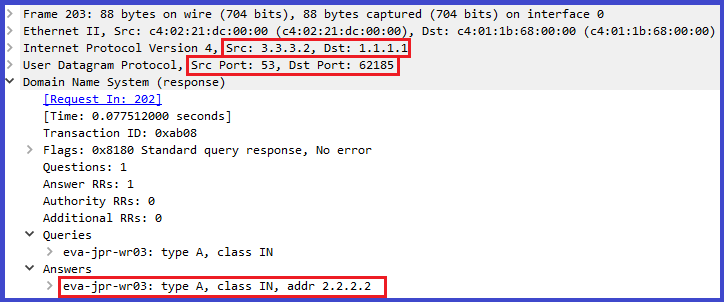
2) DNS query/Response packet has below info:
4) Once Source receives the resolved IP address of the destination , it creates a Telnet packet and
gives the telnet packet to a process running in our device called TCP. In same way TCP handovers TCP Packet to an IP process where IP put its own info on top of TCP Packet like Source and destination IP address which used of routing over internet.In same way IP handovers the packet to network access/network interface layer where system encapsulates the IP packet between an Ethernet header and Ethernet trailer, creating an Ethernet frame.
5) Destination do de-encapsulation means remove ethernet/IP/TCP header information and hands it over to TELNET process and sends a response back in the similar steps. we can co-relate with browsing as well.
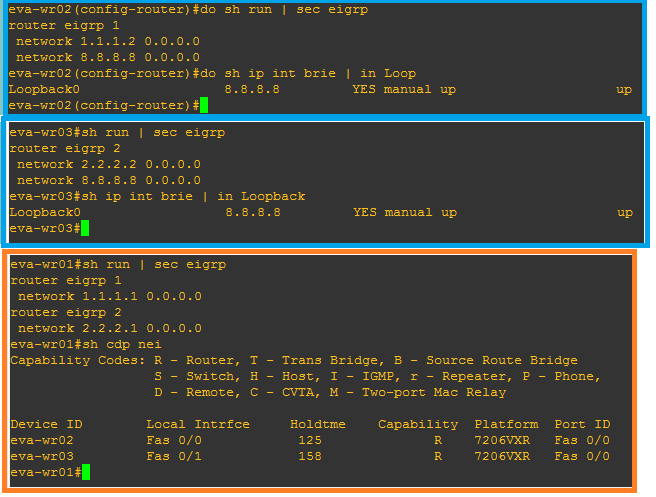
what will happen if we run 2 different eigrp processes/AS, and both AS are injecting same route with same metric?
Ans: Ans: The router installs the route that was learned through the EIGRP process with the lower Autonomous System (AS) number.
To understand this please have a close look into below topology: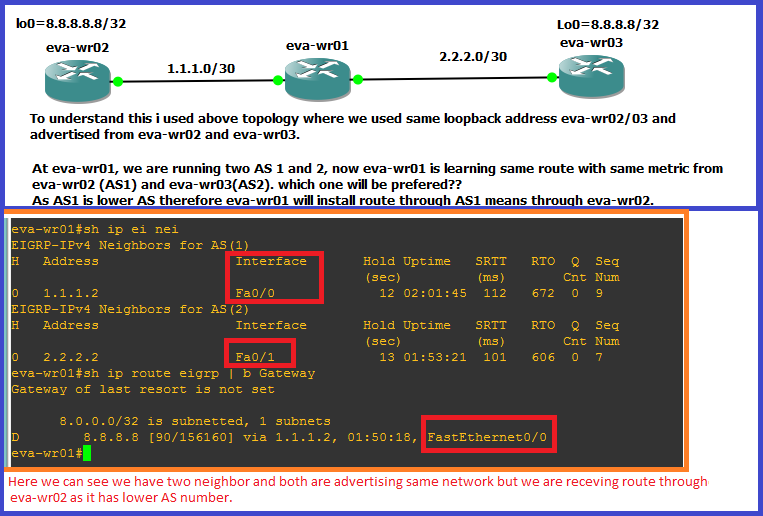
this website is very good and gives knowledge in depth. language is very simple and logics are explained with the help of configuration example and packet captures.
Really a very good and helpful
Great explanation
Like!! Great article post.Really thank you! Really Cool.
Really informative blog article.Really thank you! Want more.
I’d like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing this blog. I really hope to view the same high-grade content from you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own blog now 😉
I discovered your site web site on bing and appearance a few of your early posts. Maintain inside the very good operate. I recently additional up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Looking for forward to reading much more from you at a later date!…