Categories
RoutingPIM:
Multicast routing protocol has goal to route the multicast traffic from source to interested receiver. The protocol is named protocol-independent because it is not dependent on any particular Unicast routing protocol for topology discovery.
Multicast Tree is a topology of links where multicast traffic can flow or we can say that multicast tree is used to determine how traffic is routed from source to receiver.
There are two modes of PIM:
- Dense Mode
- Sparse Mode
Here we are going to discuss PIM Sparse mode which is referred as Pull model means In PIM-SM receiver must explicitly choose to join a multicast stream. PIM-SM uses both shared trees and Source based tree.
Let’s take below example: UPDATE topology
Source will singal to FHR about their existence and this occurs in Data Plane. Receiver will inform to LHR about their existence via IGMP or interface configuration.
As per topology FHR knows about the source and LHR knows about receiver but challenge is to connect LHR and FHR.
PIM Sparse mode operation:
- Discover PIM Neighbors and elect DR.
- Discover RP
- Tell RP about Receiver
- Tell RP about Source
- Build shared tree from sender to receiver through RP.
- Join shortest path tree
- Leave shared tree
- Multicast table maintenance
PIM uses “Hello” Messages to discover directly connected neighbor. Here is packet demo
What is role of RP?
RP is used as a reference point or central registry point which will receive multicast route info from both FHR and LHR then compare these info and work to connect them on need bases.
Shared Tree Or RP Tree Or Core Tree : Path from Receiver to Root. Number of shared tree depends on number of receiver and their location.
- Knowledge of RP
- Device should know how to reach the RP (Unicast route to RP)
- Atleast one request from a Multicast Receiver.
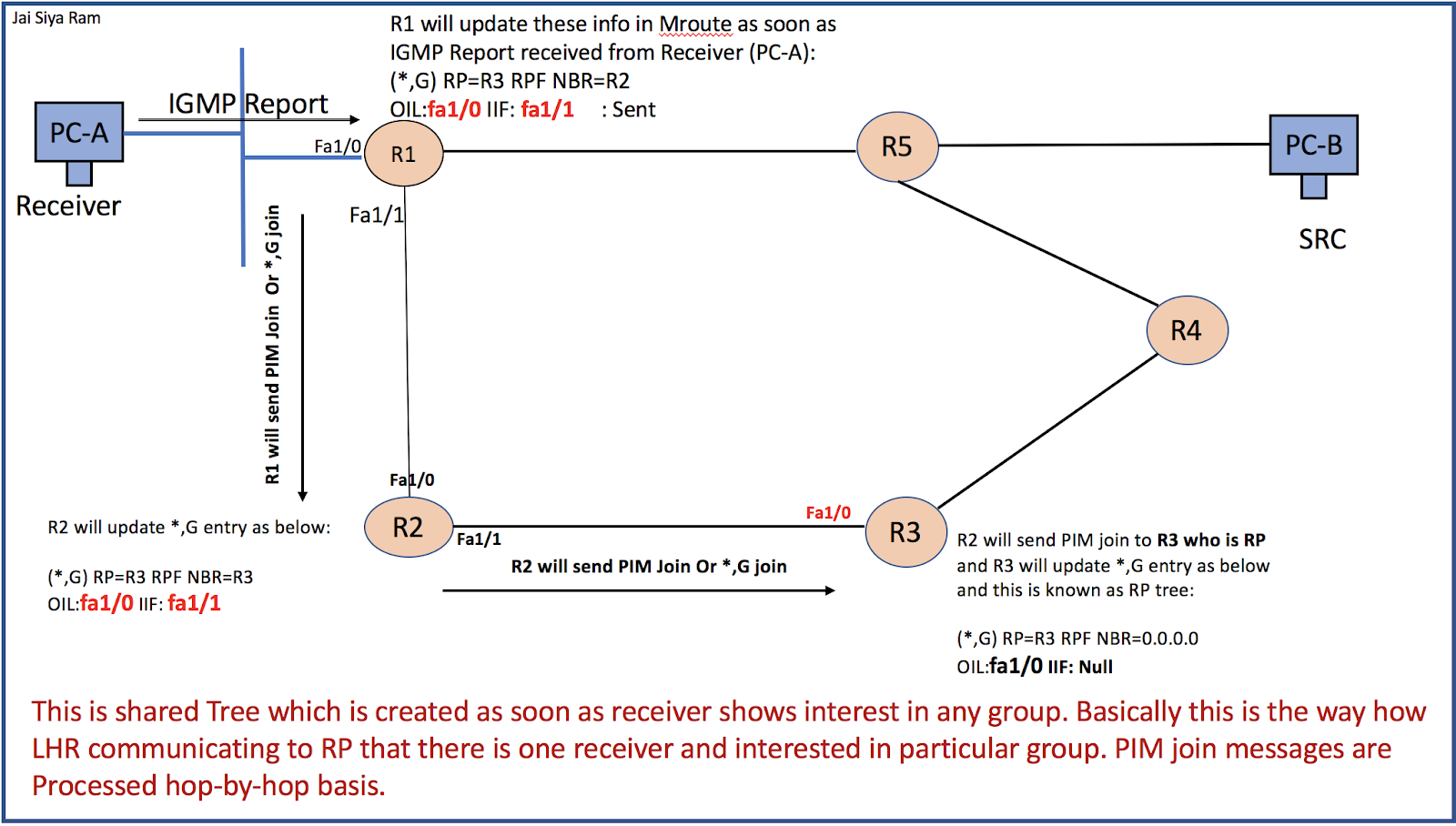
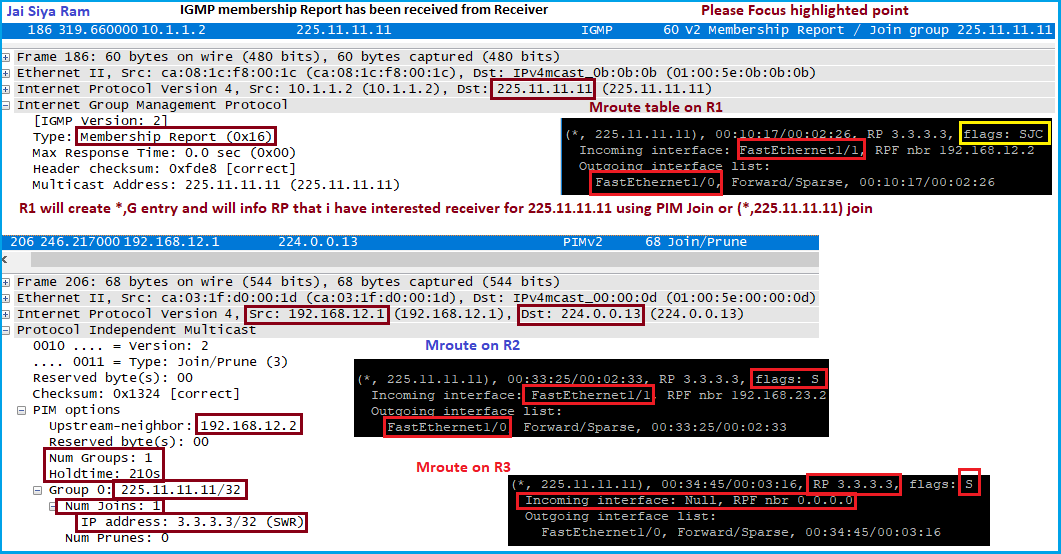
- Receiver will send membership report (saying that i am interested in group G). LHR (R1) will come to know that it has receiver on particular interface. LHR will create (*, G) entry and will update OIL.
- LHR needs to let it know to RP so RP can send stream to LHR whenever it has for group “G”. LHR sends PIM join message or *,G Join towards RP.
- Intermediate router will create (*,G) entry and update other info like OIL and forward the PIM join towards RP based on unicast route info which can be verified using “show ip rpf <RP-Address>”. Basically PIM join or *,G join is proceed hop-by-hop bases.
- RP tree is being built in reverse from leaves (LHR) to Root (RP).
- Interface receiving the PIM join or *,G join in included in OIL.
- RPF interface to RP becomes the IIF.
- Other than above things we noticed that multicast routing table has been created.
What is trigger for installation of mroute?
- IGMP Membership Report or Receiving PIM Join or (*,G) Join?
- Receiving Multicast traffic
- Dynamic or Automatic creation?
Packet capture for the same 😛
Shortest Path Tree:
So far we understood that how shared tree is build between LHR (or basically receiver) and RP. Now we have to connect source and RP so multicast traffic can flow down the tree towards receivers. To achieve this we are going to use Shortest Path Tree where FHR will let RP know that i have source which is sending particular stream. Let’s take same example:
Topology needs to be updated
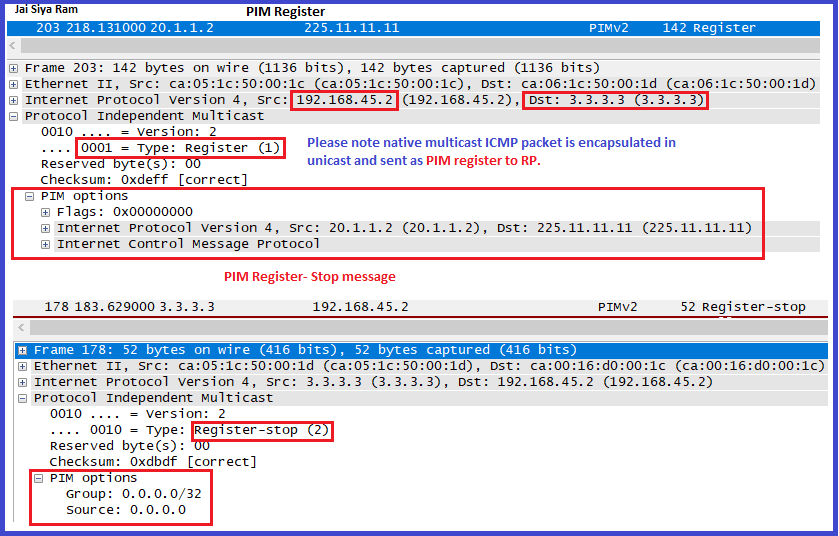
- When R5 receive multicast traffic from Source it will create (S,G and *,G) entry but OIL will be null as no one asked about stream yet. FHR (R5) will send PIM-Register Message to RP which is encapsulated in unicast.
- Intermediate router will simply forward PIM-Register messages but will not process means mroute will not be created on middle hop routers.
- When the RP receives this packet it will de-encapsulate the PIM register message and will do below:
- A. RP will create (S,G) entry with OIL and IIF.
- B. RP will send (S,G) PIM join message towards FHR as well as forward traffic using shared Tree. Intermediate router will receive (S,G) Join message and will create Mroute entry.
- C. RP will send register stop message.
What will RP do with PIM register message if no one asked for particular steam yet?
What will happen if we have multiple equal path to source?